Understanding the Role of a Videographer
What is a Videographer?
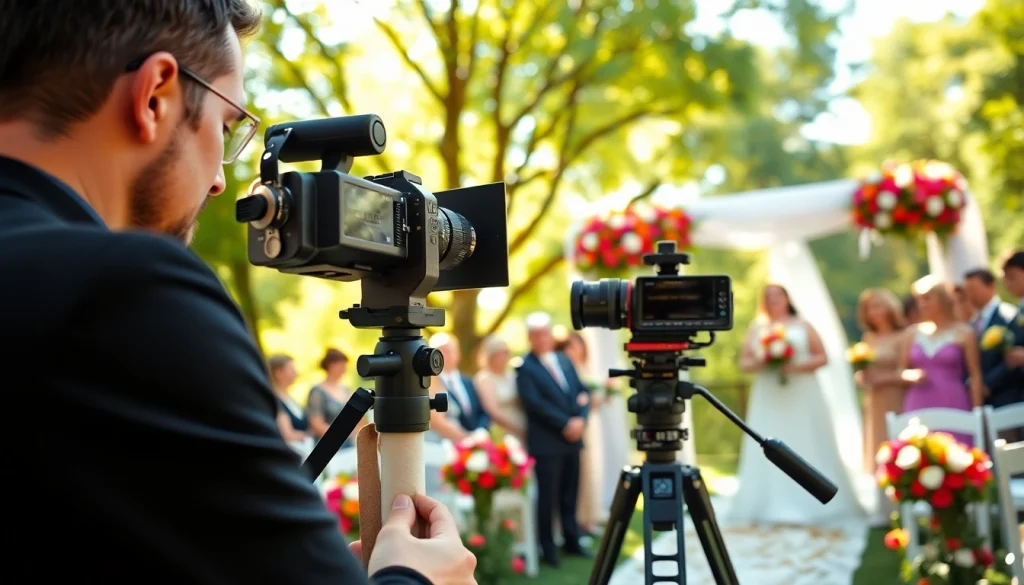
A Videographer is a professional who specializes in capturing moving images and sounds to create visual narratives. This role blends artistic creativity with technical expertise to produce films, promotional videos, documentaries, live event coverage, and more. These skilled individuals may work independently or as part of a larger production team, highlighting their versatility in various settings. The tasks they undertake often range from filming and directing to editing and post-production, showcasing a comprehensive skill set that caters to diverse project needs.
Different Types of Videographers
Videographers can be classified into several categories based on the nature of their work and the industries they serve:
- Event Videographers: Specialize in capturing significant events such as weddings, corporate gatherings, and parties. Their role involves attending events, adapting to changes on the spot, and ensuring that they document pivotal moments.
- Corporate Videographers: Focus on creating promotional content, training videos, or internal communications for businesses. Their work requires an understanding of the company’s branding and messaging objectives.
- Documentary Videographers: Engage in capturing real-life stories and events for non-fiction films. This type of videographer often conducts interviews and chronicles stories to create compelling narratives.
- Commercial Videographers: Create advertisements and marketing videos, necessitating a strong grasp of brand strategy and audience engagement.
- Freelance Videographers: Operate independently and may take on various projects across different domains, offering flexibility and a broad portfolio.
Core Responsibilities of a Videographer
While specific duties may vary by project, some core responsibilities of a videographer include:
- Pre-Production Planning: Engaging in discussions with clients to determine project goals, timelines, and necessary resources.
- Filming: Utilizing various equipment to capture high-quality video footage. This may involve setting up scenes, adjusting lighting, and ensuring sound quality.
- Post-Production Editing: Editing raw footage using industry-standard software, incorporating effects, and syncing audio to produce a polished final product.
- Collaboration: Working closely with directors, producers, and other team members to ensure that the vision of the project is realized effectively.
- Client Interaction: Maintaining communication with clients throughout the process to accommodate feedback and make necessary adjustments.
Skills Required for a Successful Videographer
Technical Skills
Technical proficiency is essential for videographers. Key technical skills include:
- Camera Operation: Understanding how to use different types of cameras, including DSLRs, camcorders, and professional cinema cameras.
- Lighting Techniques: Mastering various lighting setups to enhance the visual quality of footage.
- Sound Recording: Knowledge of audio equipment and techniques, including microphones and sound mixing, to ensure clear sound quality.
- Editing Software: Familiarity with industry-standard editing tools like Adobe Premiere Pro, Final Cut Pro, or DaVinci Resolve to produce a refined final product.
Creative Skills
Creativity plays a pivotal role in videography. Important creative skills include:
- Storytelling: The ability to craft narratives that resonate with audiences, transforming raw footage into cohesive and engaging stories.
- Visual Aesthetics: An eye for visual composition, color grading, and overall cinematic style that enhances storytelling.
- Innovation: Staying receptive to new ideas and techniques to keep content fresh and appealing in a competitive market.
Communication and Interpersonal Skills
Effective communication is critical for a videographer, as they often collaborate with clients and other professionals. Key communication skills include:
- Interpersonal Communication: Building rapport with clients, talent, and crew members to facilitate smooth interactions during projects.
- Active Listening: Understanding client needs and feedback to tailor projects accordingly.
- Presentation Skills: Clearly conveying project ideas and progress to clients and stakeholders, enhancing project engagement.
Equipment Essentials for Every Videographer
Cameras and Lenses
The backbone of a videographer’s toolkit is their camera equipment. Essential cameras and lenses include:
- Cameras: DSLRs, mirrorless models, and dedicated video cameras should cater to the range of projects a videographer might undertake.
- Lenses: A variety of lenses, including wide-angle, telephoto, and prime lenses, help achieve different visual effects and perspectives.
Audio Equipment
High-quality sound is critical in video production. Essential audio equipment includes:
- Microphones: Lavalier mics for interviews, shotgun mics for directional sound, and handheld mics for multimedia projects.
- Audio Recorders: Independent recorders to capture high-fidelity sound separate from the camera for greater flexibility in editing.
Editing Software
A proficient videographer must be adept at using editing software. Popular options include:
- Adobe Premiere Pro: A comprehensive editing suite with advanced features suitable for both amateurs and professionals.
- Final Cut Pro: A user-friendly editing software favored by many Mac users for its powerful capabilities.
- DaVinci Resolve: Known for its exceptional color grading features, making it a favorite among cinematic videographers.
How to Market Yourself as a Videographer
Building an Online Portfolio
In the digital age, an online portfolio is vital for showcasing your work. To create an impactful portfolio:
- Curate Your Best Work: Include a diverse selection of projects that highlight your skills and versatility.
- Use High-Quality Footage: Ensure that all videos are of high quality—both visually and audibly—to reflect professionalism.
- Write Contextual Descriptions: Provide details about each project, explaining your role, the creative process, and the final outcome.
Networking and Collaboration
Networking is crucial for growth as a videographer. Strategies include:
- Join Professional Groups: Engage with communities in videography and film production to share ideas and opportunities.
- Attend Industry Events: Participate in workshops, seminars, and conferences to meet potential collaborators and clients.
- Collaborate: Partner with others in the industry to broaden your skill set, gain experience, and expand your network.
Utilizing Social Media Platforms
Social media offers a powerful platform to promote your work. Consider:
- Create Engaging Content: Share snippets of your videos, behind-the-scenes footage, and insights into your creative process.
- Engage with Your Audience: Respond to comments, share experiences, and build a community around your work.
- Use Hashtags Strategically: Using appropriate hashtags can help you reach a wider audience and attract new clients.
Career Advancement Tips for Videographers
Continuous Learning and Development
The landscape of videography is constantly evolving, making continuous learning essential. Ways to further your knowledge include:
- Online Courses: Engage in courses that cover filmmaking techniques, software training, or industry specific trends.
- Workshops: Attend hands-on workshops to build practical skills and network with trainers and peers.
- Industry Certifications: Acquire certifications that establish your expertise and credibility within the field.
Seeking Feedback and Improvement
Feedback is a powerful tool for growth. Strategies to seek feedback include:
- Client Reviews: Encourage clients to provide reviews and testimonials that can inform your approach and improve your services.
- Peer Feedback: Collaborate with fellow videographers for constructive criticism on your work.
- Self-Assessment: Regularly review your own work to identify strengths and areas for improvement.
Staying Updated with Industry Trends
Keeping up with industry trends can give you a competitive advantage. Methods to stay informed include:
- Follow Industry Leaders: Subscribe to blogs, YouTube channels, and podcasts by industry experts to gain insights into current trends.
- Engage with Online Communities: Participate in discussions on platforms like Reddit or Facebook groups to exchange ideas and information.
- Experiment: Trial new techniques or equipment to stay ahead of the curve and integrate innovative elements into your work.